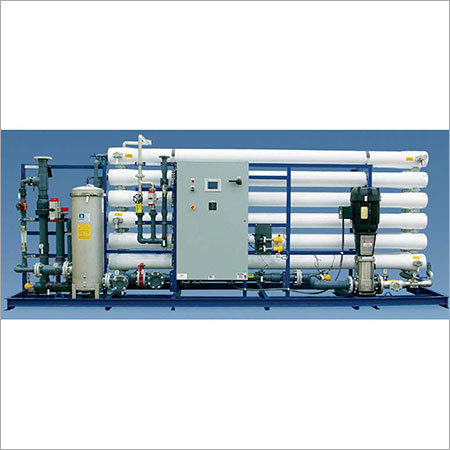
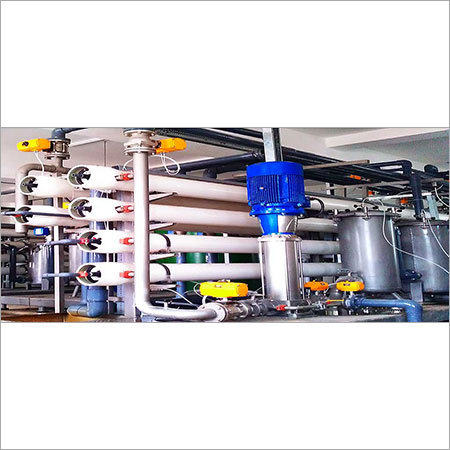
Dissolved Air Flotation System
Dissolved Air Flotation System Specification
- Ph Level
- 6.5-8
- Pump Type
- Centrifugal Pump
- Recycle Rate
- 80-90%
- Frequency
- 50 Hz
- Flow Rate
- 2-100 m/h
- Technology
- Dissolved Air Flotation (DAF)
- Power Consumption
- 2.2 kW
- Water Out Conductivity
- 50 S/cm
- Noise Level
- <70 dB
- Efficiency (%)
- 95%
- Water in conductivity
- 1000 S/cm
- Feature
- High solid removal; Compact design; Low maintenance
- Usage & Applications
- Industrial wastewater pre-treatment, Municipal water treatment, Food & beverage, Textile, Chemical plants
- Water Source
- Industrial Wastewater
- Voltage
- 380 V
- Volume
- 5 m/h
- Drive Type
- Motor Driven
- Power Source
- Electric
- Product Type
- Dissolved Air Flotation System
- Purity Level
- Up to 99%
- Automatic Grade
- Automatic
- Material
- Stainless Steel 304/316
- Filter Type
- Microbubble Separation
- Capacity
- 2-100 m/h (customizable)
- Installation Type
- Floor Mounted
Dissolved Air Flotation System Trade Information
- Minimum Order Quantity
- 1 Unit
- Main Export Market(s)
- Africa, Asia
- Main Domestic Market
- All India
About Dissolved Air Flotation System
DISSOLVED AIR FLOTATION(DAF) SYSTEM
Dissolved Air Flotation is a liquid/solid separation process in which microscopic air bubbles (10-100) become attached to solid particles suspended in liquid, causing the solid particles to float. In a DAF system air is dissolved into liquid under pressure. The dissolved air remains in solution until the pressure is released to atmospheric pressure, causing the air to come out of solution in the form of microscopic air bubbles. The bubbles are mixed intimately with the waste water and become attached to the solids in the waste stream causing the air solids.
Agglomerate to float to the liquid surface where a solids (float) blanket is formed. Surface skimmers then remove the float blanket.
ADVANTAGES OF DISSOLVED AIR FLOTATION (DAF) SYSTEM
Dissolved air flotation (DAF) has gained widespread usage over the last forty years for the removal of suspended solids (TSS), oils and greases (O&G), and biochemical oxygen demand (BOD) from waste water and other industrial process streams. DAF systems are frequently used to provide waste water pretreatment, product recovery, and thickening of biological solids in industries ranging from food processing to pulp and paper to petrochemicals. Years of experience in specifying DAF systems for industrial applications has shown that many engineers, designers, and end users have come to rely on DAF design information from common reference materials, such as engineering handbooks. Such reference materials base specification of DAF systems on parameters such as recycle rate and pressure, air-solids ratio, hydraulic loading, and surface loading. However, the values provided in common references for these parameters tend to be outdated or inadequate when compared to data from actual operating systems.
In other words, the reliability and performance of DAF systems have improved with increased use of this technology, but there has not been a corresponding change in the standard design criteria for these systems.
DAF OVERVIEW
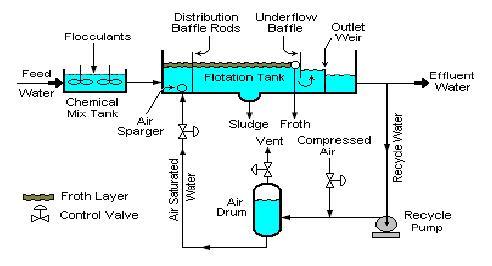
While DAF units come in many forms, the systems most commonly produced today are Circular-shaped units using recycle pressurization to provide dissolved air to encourage flotation. As illustrated in Figure 1, a DAF system consists of the following primary components:
Contact cell or coagulation chamber. Provides for the mixing of dissolved air with flocculated particles in the influent to allow for attachment of bubbles to particles. Also provides even distribution of flow across the width of the unit.
Flotation cell. Provides surface area for the flotation of air and flocculated particles (float).
Surface skimmer. Provides the means for removal of float from the flotation cell for transfer to dewatering or other handling. The most Commonly-used system involves a series of flights pulled by a chain drive system with variable-speed, timer-operated drives.
Bottoms skimmer or auger. Provides for the removal of settled solids in the bottom of the unit.
Effluent discharge baffle and chamber. Provides for physical separation of clarified water from flocculated particles and bottoms prior to discharge from the unit through weirs or similar structures.
Air saturation (whitewater) system. Provides the required amount air in the proper form (bubble sizes in the range of 10-100 m), ideally using minimum recycle flow. The whitewater system uses pump pressurization to force air into solution with either the influent stream or a clarified effluent recycle stream. The air-water solution is then injected into the incoming waste water stream to encourage bubble-solid contact and flotation.
Efficient Microbubble Separation Technology
The DAF system utilizes pressurized air with microbubble nozzles, maximizing solid separation from wastewater. Microbubbles attach to suspended particles, enabling rapid and effective floc formation and removal, resulting in high clarity and efficient contaminant extraction. This process achieves a purity level of up to 99%, making it ideal for demanding industrial applications.
Automated Operation and Monitoring
Controlled by a PLC-based operation panel, the system ensures reliable, hands-free operation. Automatic sludge discharge, digital water level monitoring, and precise conductivity control streamline maintenance and reduce manual intervention. Designed for continuous operation, the DAF systems motor-driven mechanisms maintain efficiency, and low noise output ensures suitability for a variety of installation locations.
FAQs of Dissolved Air Flotation System:
Q: How does the Dissolved Air Flotation System achieve high solid removal efficiency?
A: The system employs pressurized air with microbubble nozzles, which generate fine bubbles that attach to suspended solids and push them to the surface for effective separation. This process, in conjunction with precise flow control and automatic sludge discharge, ensures an efficiency rate of 95% and purity levels up to 99%.Q: What is the recommended pre-treatment for water entering the DAF system?
A: Screening is recommended as a pre-treatment step to remove large debris and protect the DAF system from clogging or reduced performance. This helps maintain optimal flow and maximizes the efficiency of microbubble separation during operation.Q: When is it necessary to customize the inlet/outlet size or capacity of the system?
A: Customization is required when application parameters such as flow rate, inlet/outlet pipe sizes (DN50DN200), and treatment capacity (2100 m/h) differ from standard configurations. For specific industry requirements, these adjustments ensure effective integration and optimal system performance.Q: Where can this DAF system be installed?
A: This system is designed for floor-mounted installation, requiring a surface area of 1025 m. It suits industrial facilities, municipal water treatment plants, food processing factories, textile operations, and chemical plants across India.Q: What are the benefits of using an automatic grade, PLC-controlled DAF system?
A: The automatic grade system with PLC control offers hands-free operation, minimal maintenance, accurate digital level monitoring, and controlled sludge discharge. These features enhance operational reliability, improve process consistency, and reduce downtime, leading to overall cost savings and streamlined wastewater management.Q: How does the DAF system support environmental sustainability in wastewater treatment?
A: With a recycle rate of 8090%, the DAF system conserves water resources by allowing treated water to be reused. Its high solid removal capacity minimizes harmful discharge, supporting regulatory compliance and environmental protection initiatives.Q: What types of industrial wastewater can the DAF system treat?
A: The DAF system is suitable for a wide range of wastewater sources including industrial discharge, municipal water, food and beverage processing effluents, textile and chemical plant wastewater. Its customizable features ensure suitability for various pollutant concentrations and flow rates.

Price:
- 50
- 100
- 200
- 250
- 500
- 1000+
More Products in Waste Water Treatment Plant Category
Salt Recovery Plant (Nano Filtration System)
Minimum Order Quantity : 1 Unit
Feature : Low operating cost, High recovery ratio, Reduced sludge generation
Product Type : Salt Recovery Plant Nano Filtration System
Water Source : Other, Industrial Effluent, Brine, RO Rejects
Material : Stainless Steel (SS 304/316)
Usage & Applications : Salt recovery, Waste water treatment, Industrial water recycling
Waste Water Desalination
Minimum Order Quantity : 1 Unit
Feature : High recovery, Low maintenance, Skid mounted, User friendly interface
Product Type : Desalination Plant
Water Source : Other, Industrial Waste Water / Brackish Water / Municipal Wastewater
Material : Stainless Steel, FRP, PVC
Usage & Applications : Industrial water treatment, Effluent recycling, Desalination of sewage and brackish water
Zero Liquid Discharge Plant
Minimum Order Quantity : 1 Unit
Feature : Low Maintenance, High Recovery Rate, Energy Efficient, Environment Friendly
Product Type : Zero Liquid Discharge Plant
Water Source : Other, Industrial Effluent, Municipal Wastewater, RO Reject
Material : SS304/SS316, FRP, Mild Steel with Epoxy Coating
Usage & Applications : Industrial Wastewater Treatment, Effluent Recycling, Textile, Chemical, Pharma, Power Plants
Zero Liquid Discharge
Minimum Order Quantity : 1 Unit
Feature : Complete elimination of liquid waste
Product Type : Water Treatment System
Water Source : Industrial wastewater, Other
Material : Stainless Steel
Usage & Applications : Industrial wastewater management

 Send Inquiry
Send Inquiry Send Inquiry
Send Inquiry




